How to Make a Simple Solenoid Engine?
Assalamualaikum and hi there! Today, I’m excited to share my ICT Multimedia Project from secondary school. Presented using Microsoft Movie Maker, this project is what I call a Simple Solenoid Engine. I picked this topic because it’s a fun, hands-on introduction to basic engineering principles—and honestly, I had plenty of paperclips lying around! 😅
It was challenging initially, but after some trial and error, I realized how simple (and fun) it could be. My work was inspired by this video and others like it. While their versions were cooler and more polished, I decided to create my own tutorial to help others. Let’s dive in!
What is a solenoid engine?
A solenoid is a coil of wire wrapped around a cylindrical shape. When an electric current flows through it, an electromagnetic field is generated. Think of it as a temporary magnet, activated only when powered.
Here’s a simple diagram for reference:
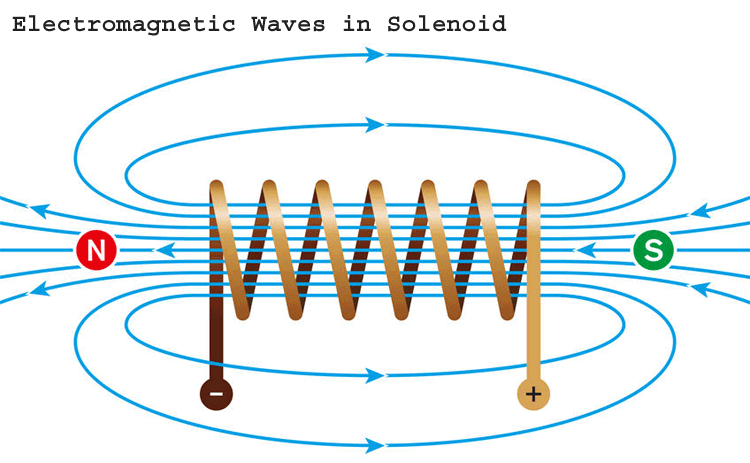
Blue arrow = Magnetic field direction (North to South)
Plus to Minus = Current flow through the wire
Breaking it down:
- A solenoid generates a magnetic field when electricity flows through it.
- An engine is a device that converts energy into motion.
- A solenoid engine uses a coil to create a magnetic field, pulling a small magnet (the "piston") to generate mechanical motion.
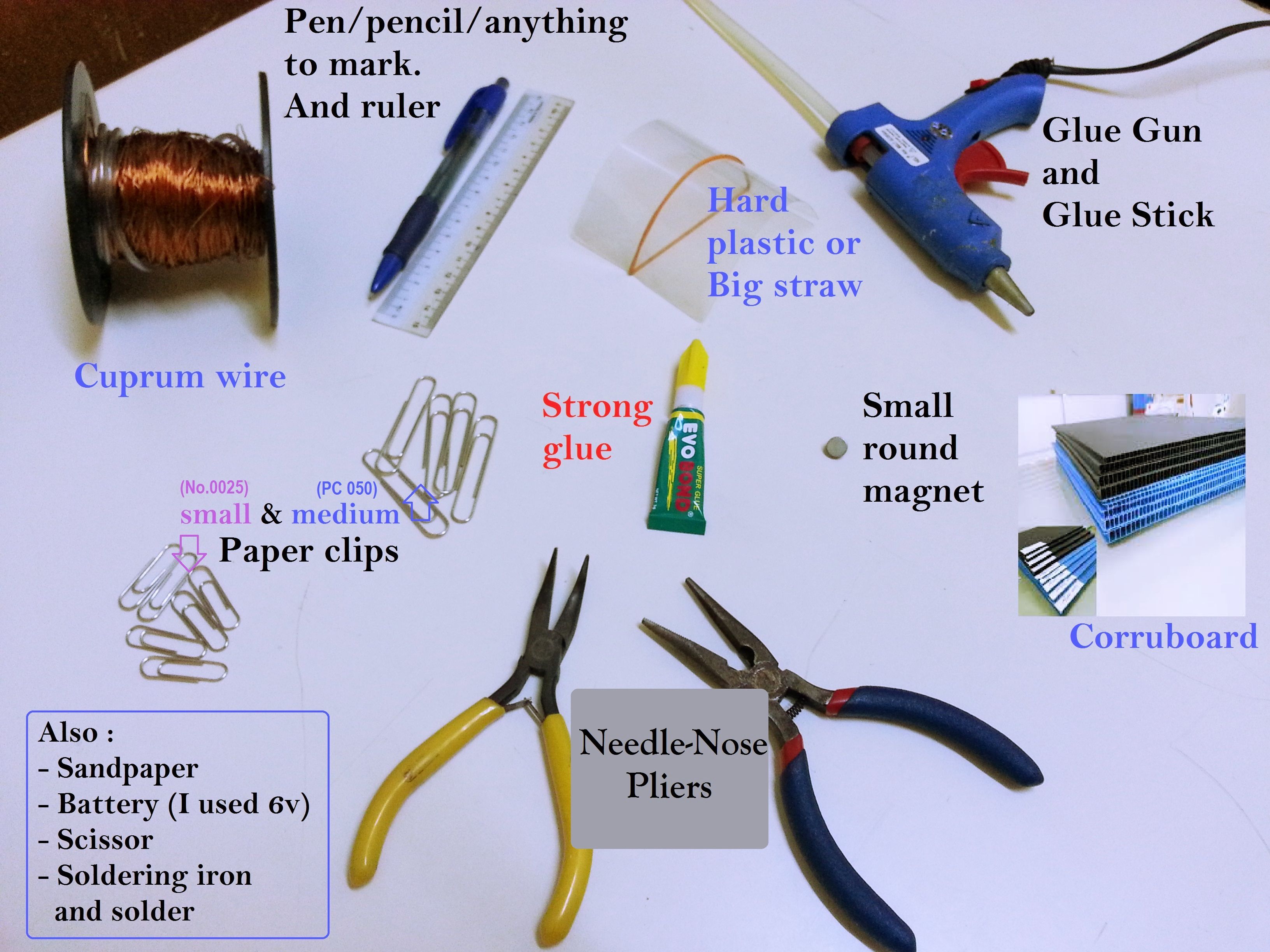
What do we need to make a simple solenoid engine?
Tools:
- Glue gun & hot glue sticks
- Scissors
- Ruler
- Needle-nose pliers
- Pen/pencil/marker
Materials:
- Small paper clips (No. 0025)
- Large paper clips (PC 050)
- Copper wire
- Laminating sheet, large straw, or thin hard plastic
- Small round neodymium magnet
- 6V battery (or 4 x 1.5V batteries + holder)
- Strong glue
- Hollow board sheet
- Sandpaper
How does it work?
Before we jump in, let’s understand how this solenoid engine operates. Knowing the mechanics will help you refine your design (like the on/off switch). Here’s the final product:
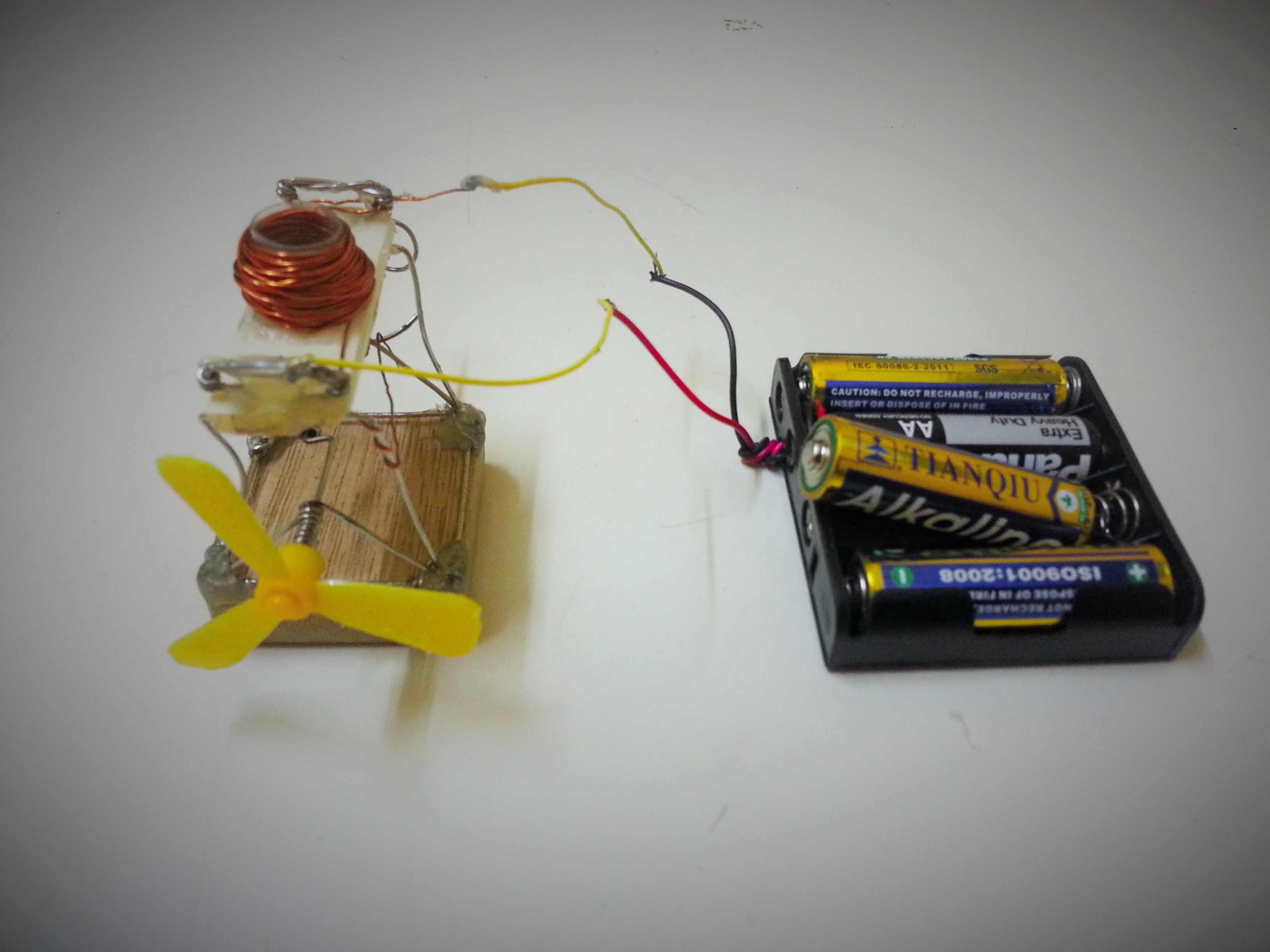
The process:
- At Rest: The piston (small round magnet) is at the bottom. The circuit closes (switch on), allowing current to flow. The solenoid generates a magnetic field.
- Magnet Attraction: The piston is pulled upward by the magnetic field.
- Switch Off: As the piston rises, the circuit opens (switch off), stopping the current and deactivating the solenoid. Gravity pulls the piston back down.
- Repeat: Steps 1–3 continue, powered by a steady energy source (e.g., batteries). The piston’s motion generates rotational mechanical energy.
Factors Affecting Magnetic Field Strength

Several factors influence the strength of the solenoid’s magnetic field:
- Number of Turns: More wire turns = stronger magnetic field.
- Soft Iron Core: Enhances the field strength.
- Current Flow: Higher current = stronger magnetic field.
- Wire Thickness: Thicker wire supports a stronger field.
Ready to Build?
Follow the steps in this tutorial and let your creativity flow! Don’t worry about perfection—enjoy the process and learn as you go. Also, don’t stress about the "I ❤️ PaperClips" part—it’s just a fun touch! If you find this helpful, be sure to like, share, and comment. 😊
This tutorial is available on YouTube.
References
- Memory Booster (Physics Book - Form 5, Chapter 3)
- Fokus U SPM Fizik



